The Ultimate Guide to Flash Floods: Safety, Awareness, and Preparedness
Flash floods are sudden, powerful, and often devastate communities with little warning. This comprehensive guide covers everything you need to know, from safety measures to understanding the science behind flash floods.
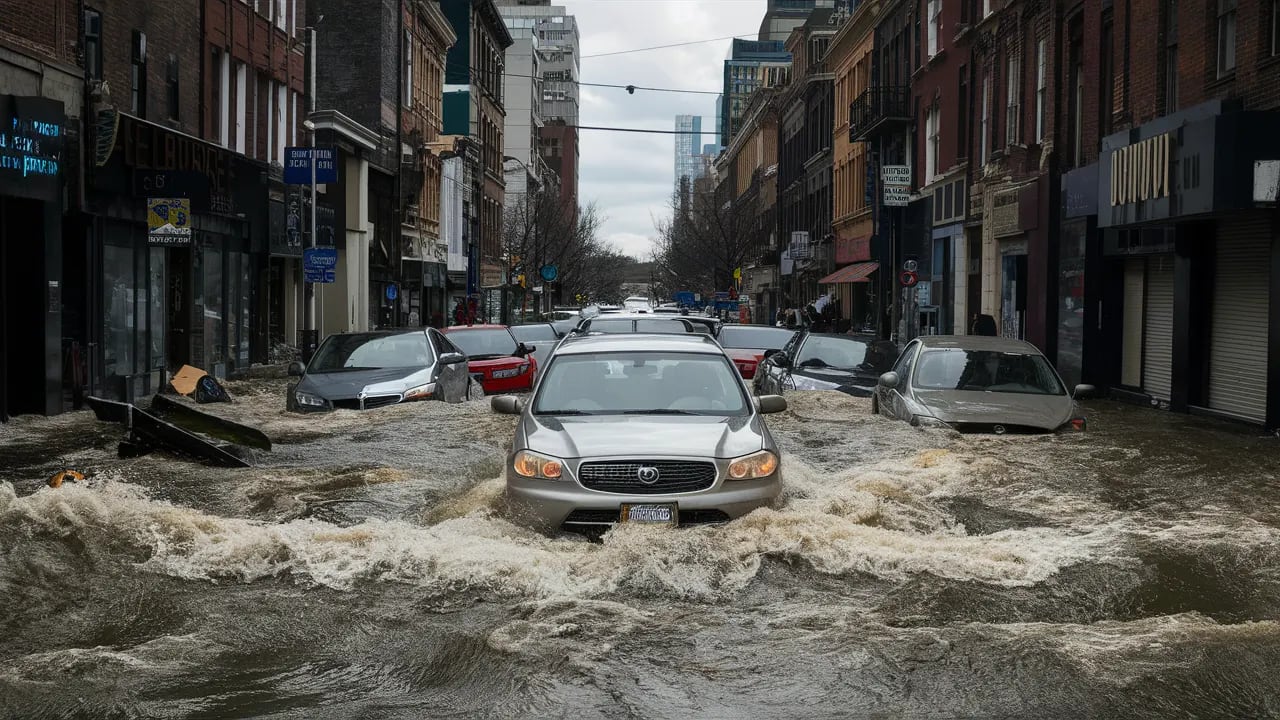
Flash floods are unpredictable beasts, arriving with little warning and wreaking havoc on communities. In 2021 alone, flash floods accounted for over $2 billion in damages in the U.S. and claimed the lives of numerous individuals. These terrifying events can transform a peaceful setting into a torrent of destruction within minutes.
In this blog post, we’ll delve into every aspect of flash floods to help you understand what they are, how to stay safe during one, and the underlying science that makes them both fascinating and dangerous. We’ll answer numerous practical questions to help you be prepared for these sudden events. From recognizing early signs to understanding their long-term effects, this guide covers it all.
What is a Flash Flood?
Flash Flood Definition and Overview
A flash flood is a sudden and rapid flooding event typically caused by heavy rainfall over a short period, usually less than six hours. Unlike regular flooding, which develops gradually, flash floods can strike with little to no warning, often sweeping away everything in their path.
Table: Flash Flood Characteristics
What Causes Flash Floods?
Flash floods result from various meteorological and geographical factors:
- Intense Rainfall: When rain falls too quickly for the ground to absorb.
- Dam Breaks: Sudden release of water due to dam or levee failures.
- Snowmelt: Rapid melting of snow combining with rain.
- Urbanization: Impermeable surfaces like roads and buildings increase runoff.
Flash Flood Definition in Geography
In geographic contexts, flash floods typically affect areas with poor absorptive capacity, such as urban environments or arid regions.
What Should You Do During an Intense Flash Flood?
Immediate Actions to Ensure Your Safety
- Seek Higher Ground: Move immediately to higher ground; avoid low-lying areas.
- Avoid Water: Never walk or drive through floodwaters. Just six inches of water can knock you off your feet.
- Stay Informed: Listen to weather alerts and follow any evacuation orders.
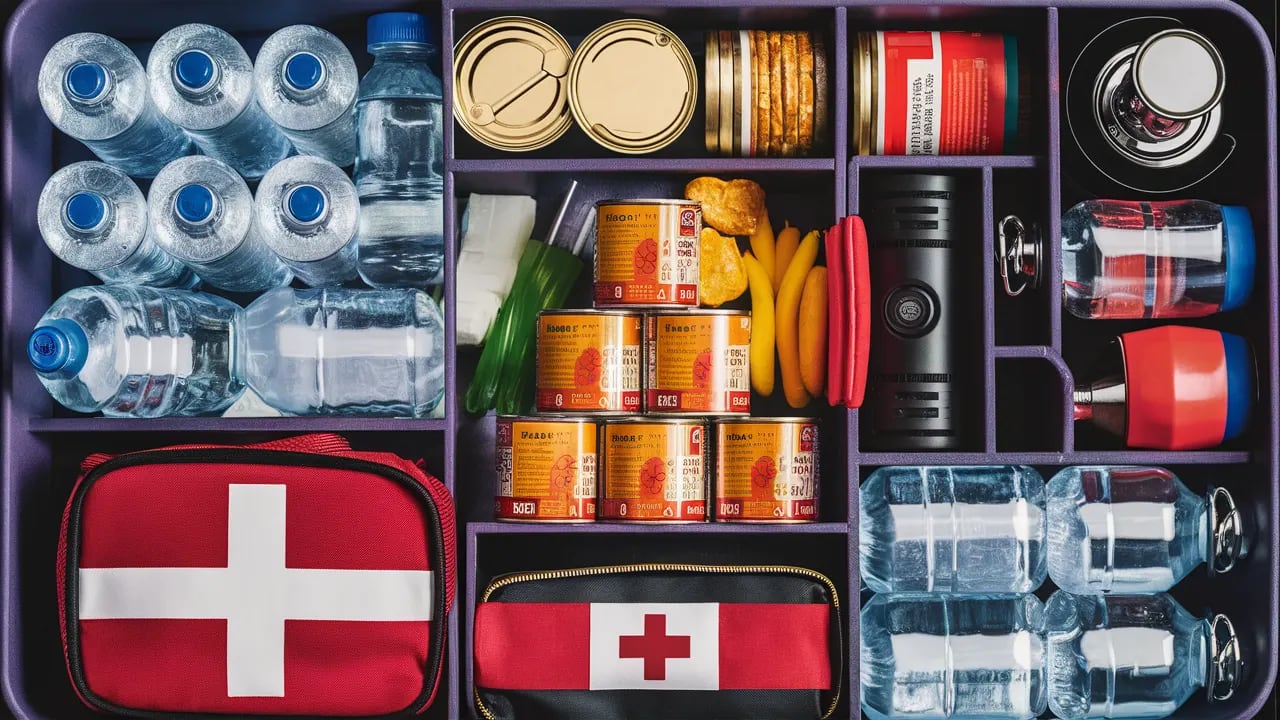
- Prepare an Emergency Kit: Include essentials like water, non-perishable food, a flashlight, and a first-aid kit.
- School and Business Preparedness: Ensure emergency response plans are in place, conduct regular drills, and maintain effective communication systems.
”Your best chance of survival during a flash flood is to act quickly and decisively.” - National Weather Service
Are Flash Floods Predictable?
Understanding Predictability and Forecasting
Flash floods are notoriously difficult to predict with precision due to their rapid onset and localized nature. However, advancements in meteorological technology have improved early warning systems. Tools like Doppler radar and satellite imagery help meteorologists identify conditions conducive to flash floods.
- Technologies Used:
- Doppler Radar: Detects intense rainfall and storm conditions.
- Satellite Imagery: Provides visual data on weather patterns.
- Hydrological Models: Predict river flow and runoff.
- Real-time Weather Data: Monitors rainfall and storm developments.
How Alerts Are Issued
Flash Flood Warnings are typically issued when a flash flood is imminent or occurring. The National Weather Service and other meteorological agencies rely on:
- Real-time Weather Data: Radar and rain gauges.
- Hydrological Models: Predict river flow and runoff.
- Storm Tracking: Monitors storm development and movement.
How Much Rain Can Fall in a Flash Flood?
Rainfall Intensity and Measurement
The amount of rain that falls during a flash flood varies, but it can be as much as 10 inches in a few hours. This intense rainfall quickly overwhelms natural and artificial drainage systems.
Table: Examples of Flash Flood Rainfall
What Areas of the World Are on a Flash Flood Watch?
Global Hotspots for Flash Floods
Flash floods can occur anywhere, but some regions are more prone due to their climate, geography, and urbanization. These include:
- United States: Particularly in the Midwest, South, and Western states.
- South Asia: Monsoon rains frequently cause flash floods in countries like India and Bangladesh.
- Southeast Asia: Frequent typhoons contribute to flash flooding in countries like the Philippines.
- Europe: Mountainous regions and urban centers in countries like Germany and Switzerland.
Should I Believe the Severe Flash Floods Warning ⚠️?
The Importance of Trusting Official Alerts
Absolutely. A severe flash flood warning means that a flash flood is imminent or already happening. Ignoring such warnings can lead to catastrophic consequences, including loss of life.
”Ignoring a flash flood warning can be a fatal mistake. Take them seriously and react quickly.” - American Red Cross
Related Products for Preparedness
Flash Flood Causes
How Does Severe Weather Cause Major Floods?
Severe weather systems, including thunderstorms, hurricanes, and tropical storms, are often the precursors to flash floods. These systems produce extreme rainfall over short periods, overwhelming drainage and river systems.
Causes of Flash Floods in a Desert
Deserts, with their hard, dry soil, are particularly vulnerable. When rare heavy rains occur, the ground cannot absorb water quickly, leading to sudden and intense flooding.
How Long Do Flash Floods Last?
Duration and Aftermath
Flash floods typically last for a few hours but can cause long-term devastation. The cleanup and recovery efforts can take weeks to months, depending on the severity of the flood.
What Are the Effects of Flash Floods on Human Health?
Immediate and Long-term Health Risks
- Drowning: The primary cause of death during flash floods.
- Injuries: From debris and swift-moving water.
- Diseases: Contaminated water can spread waterborne diseases.
- Mental Health: The trauma from experiencing a flash flood can lead to anxiety, depression, and PTSD.
What is the difference between a flood watch and a flood warning?
flood watch means that conditions are favorable for flooding to occur in the area. It does not mean that flooding will definitely occur, but it is a heads up to be prepared and monitor the situation closely.
flood warning means that flooding is imminent or already occurring. This is a more serious alert that requires immediate action to protect life and property.
What should I do if a flash flood warning is issued for my area?
If a flash flood warning is issued, it means a flash flood is occurring or will occur very soon. You should evacuate immediately and move to higher ground away from rivers, streams, creeks, and storm drains. Never drive through flooded areas - turn around and find an alternate route. Act quickly as flash floods can become life-threatening within minutes.
How can I prepare for a potential flood?
Preparing for a flood:
- Create a family emergency plan and identify evacuation routes and meeting places.
- Assemble an emergency supply kit with essential items like food, water, medications, and first aid supplies.
- Purchase flood insurance, as most homeowners insurance does not cover flood damage.
- Elevate furnaces, water heaters, and electrical panels if possible.
- Clear debris from gutters and downspouts to allow proper drainage.
- Learn the difference between flood watches, warnings, and emergencies.
What supplies should I include in a flood emergency kit?
Essential supplies for a flood emergency kit:
- Water (1 gallon per person per day for at least 3 days)
- Non-perishable food and manual can opener
- Battery-powered radio and extra batteries
- Flashlight and extra batteries
- First aid kit
- Medications and medical items
- Sanitation and personal hygiene items
- Copies of personal documents
- Cell phone with chargers and backup battery
- Emergency blankets and rain gear
- Tools and supplies for securing your home
Good products to consider adding to your emergency kit:
What are some tips for staying safe during a flood?
Flood safety tips
- Avoid walking or driving through floodwaters - just 6 inches of water can knock you down, and 1 foot of water can sweep away a vehicle.
- Do not drive around barricades - the road may be washed out.
- Stay away from downed power lines and electrical wires.
- Look out for animals that may have been displaced by floodwaters.
- Listen to authorities and evacuate if advised.
- Return home only when officials say it is safe.
”Surviving a flash flood is just the beginning. The mental and physical toll can last a lifetime.” - Psychology Today
What Are the Risks of Flash Flooding in California?
California’s Unique Challenges
- Seasonal Rains: Heavy winter rains can quickly turn into flash floods.
- Wildfires: Burned areas are more susceptible to flash floods as the soil cannot absorb water effectively.
- Urban Areas: High levels of urbanization increase runoff.
Similar Events in History
- 2018 Montecito, CA: Debris flow from wildfires caused destructive flash floods.
- 1997 El Niños: Heavy rains led to numerous flash floods across the state.
How to Spot Early Signs of a Flash Flood While Hiking
Hiker’s Guide to Flash Flood Awareness
- Weather Forecasts: Always check weather forecasts before heading out.
- Low-Lying Areas: Avoid camping or hiking in canyons and low-lying areas.
- Clouds and Rain: Be cautious if you see rapidly building dark clouds and hear thunder.
- River Water Levels: Sudden increases in water level or muddy water are dead giveaways.
- Unusual River Sounds: Roaring or gurgling sounds indicating fast-moving water.
- Movement of Debris: Noticeable movement of debris in water channels.
What Are the Similarities of Flood and Flash Flood?
Comparing Types of Floods
Weather Flash Floods Today
Current Situations and Alerts
Staying updated on the current weather conditions is crucial in areas prone to flash floods. Regularly check real-time weather updates and alerts from reliable sources such as the National Weather Service (NWS), your local meteorological office, and online weather platforms. Additionally, the Optic Weather app offers personalized weather alerts, which can be invaluable in providing timely warnings about severe weather events.
Key Actions:
- Enable weather alerts on your smartphone.
- Monitor local news channels for weather updates.
- Follow social media accounts of local weather services for real-time updates.
”Being aware of real-time weather conditions can make the difference between safety and disaster in flash flood-prone areas.” - National Weather Service
What Happens If You Don’t Evacuate During Severe Flooding?
Potential Consequences
Failing to evacuate during severe flooding can lead to dire consequences:
- High Risk of Drowning: Flash floods create fast-moving water flows that can sweep away people and vehicles within seconds.
- Example: In past floods, many fatalities occurred because individuals tried to cross flooded roads or stay in their homes.
- Getting Stranded: Those who stay behind may find themselves without access to food, clean water, and medical supplies.
- Scenario: Roads can become impassable, and emergency services may be unable to reach those in need.
- Long-term Health Effects: Floodwaters can contaminate clean water supplies, leading to disease outbreaks, while the traumatic experience can cause lasting mental health issues.
- Example: Waterborne diseases like cholera can spread in the aftermath, and PTSD can affect survivors.
Key Actions:
- Always follow evacuation orders promptly.
- Have a plan in place to move quickly.
- Ensure your emergency kit is ready with essential supplies.
”Ignoring evacuation orders can be a fatal mistake. Timely evacuation is essential to survival.” - American Red Cross
What Can We Learn from the UK’s Cold Weather and Flooding?
Lessons from the UK
- Preparedness: Always have an emergency kit ready.
- Infrastructure: Invest in robust flood defenses and effective drainage systems.
- Community: Community readiness and support can improve survival and recovery rates.
Does Friendswood, TX Flood Much?
Examining Flood Risks in Friendswood, TX
Friendswood, located near Houston, Texas, is prone to flooding due to heavy rains and its proximity to rivers and bayous. The city has experienced significant flooding in recent years, making it crucial for residents to stay informed and prepared.